Intégration continue avec GitLab CI
Auteur : Francois-Emmanuel Goffinet
Date de fabrication : Wed Jan 06 2021 21:07:55 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time), v1.0
Téléchargements des supports

- 1. Introduction à GitLab
- 2. Commencer avec Gitlab
- 3. Projet de départ GitLab CI avec Pages
- 4. CI/CD Gitbook
- 5. CI/CD Jekyll
- 6. CI/CD Mkdocs
- 7. CI/CD Maven - Apache Tomcat
- 8. Projets PHP
- 9. Installation d'un serveur GitLab CE
- 10. Administration d'un serveur GitLab
- 11. Installation et configuration de Gitlab Runner
- 12. Scénario de vie / Orchestration
1. Introduction à GitLab
1.1. Projet Gitlab
GitLab est un outil de gestion du cycle de vie DevOps basé Web qui intègre un gestionnaire de référentiel Git avec des fonctionnalités wiki, de suivi des problèmes et de pipeline CI/CD. Il est développé sous licence open-source par GitLab Inc.

Le logiciel se décline en quatre produits :
- GitLab CE (Community Edition) - auto-hébergé et gratuit, support communautaire.
- GitLab EE (Enterprise Edition) - auto-hébergé et payant, fonctionnalités supplémentaires.
- GitLab.com - SaaS, gratuit ou avec abonnement.
- GitLab.io - Instance privée gérée par GitLab Inc.
Les outils comparables sont par exemple GitHub ou Bitbucket.
1.2. Introduction à DevOps avec GitLab CI
La documentation de GitLab CI sur trouve à l'adresse https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/README.html.
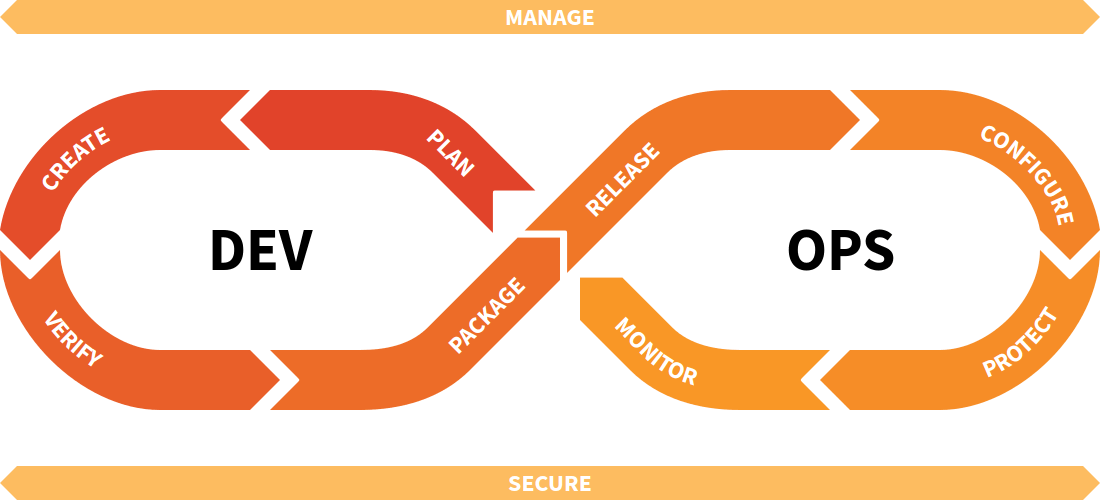
Un cycle de vie DevOps se compose de différentes étapes en boucle : "Plan", "Create", "Verify", "Package", "Release", "Monitor". De manière transversale "Manage" et "Secure" s'intéressent à toutes les étapes du cycle.

| DevOps Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Manage | Statistiques et fonctions d'analyse. |
| Plan | Planification et gestion de projet. |
| Create | Fonctions SCM (Source Code Management) |
| Verify | Tests, qualité du code et fonctions d'intégration continue. |
| Package | Registre des conteneurs Docker. |
| Release | Release et de livraison de l'application. |
| Configure | Outils de configuration d'applications et d'infrastructures. |
| Monitor | Fonctions de surveillance et de métrique des applications. |
| Secure | Fonctionnalités de sécurité. |
1.3. Points forts de Gitlab
Ses points forts sont les suivants, de manière non exhaustive :
- Modèle commercial Open Source
- Fonctionnalités et intégrations avancées
- Documentation ouverte
- Installation et maintenance aisées
- Modèle de déploiement très diversifié, évolutif
- Ergonomie pour un usage quotidien
- Permet de migrer ses référentiels Git à partir de nombreux concurrents
- Permet d'être très satisfait sans budget
- Bien d'autres sans doute
1.4. Points faibles de Gitlab
Son point faible est d'être moins populaire que GitHub.
1.5. Mises en guarde sur l'usage de Gitlab
Si l'on désire en faire un usage plutôt public ou dans le nuage (gitlab.com), Gitlab offre déjà gratuitement des fonctionnalités très avancées.
Dans tous les cas, si les utilisateurs consomment un certain seuil de ressources, il est normal d'en payer le prix, le vrai prix, souvent moins jamais plus.
Dans cette perspective une solution auto-hébergée demandera un minimum de ressources recommandées selon Gitlab :
- CPU : 4
- RAM : 4 GB
- du stockage en conséquence
Il est fortement déconseillé de faire fonctionner les Gitlab-runners (exécutants CI/CD) sur la même machine que le serveur Gitlab.
2. Commencer avec Gitlab
git - petit guide, juste un petit guide pour bien démarrer avec git. no deep shit ;)
2.1. Informations de départ
Prenez un compte.
2.2. Organize
Create projects and groups.
2.3. Prioritize
Create issues, labels, milestones, cast your vote, and review issues.
- Create an issue
- Assign labels to issues
- Use milestones as an overview of your project's tracker
- Use voting to express your like/dislike to issues and merge requests
2.4. Collaborate
Create merge requests and review code.
- Fork a project and contribute to it
- Create a new merge request
- Automatically close issues from merge requests
- Automatically merge when pipeline succeeds
- Revert any commit
- Cherry-pick any commit
2.5. Test and Deploy
Use the built-in continuous integration in GitLab.
2.6. Install and Update
Install and update your GitLab installation.
3. Projet de départ GitLab CI avec Pages
GitLab Pages est une fonctionnalité qui permet de publier des sites web statiques directement à partir d'un référentiel dans GitLab. La documentation de départ est accessible à partir de cette page : Creating and Tweaking GitLab CI/CD for GitLab Pages.
Un cycle d'intégration continue dans Gitlab CI est défini à partir d'un fichier de configuration écrit en YAML. Le fichier est placé à la racine du projet sous le nom réservé de .gitlab-ci.yml.
Un "pipeline" est une suite de "stages", soit un flux d'étapes. Un "stage" exécute des jobs. Ceux-ci sont définit par des variables, des commandes et la génération d'"artifacts". Un "artifacts" est le résultats d'une exécution gardé en mémoire pour traitement dans le "pipeline".
L'exécution des jobs sont réalisées dans des conteneurs Docker sur n'importe quel machine ou Pod K8s (Kubernetes) enregistrés comme "Gitlab Runner".
GitLab CI/CD Pipeline Configuration Reference
Un "job" spécial nommé "pages" génère tous les "artifacts" d'un site web dans le dossier spécial public.
Job spécial Pages et dossier public/
3.1. Essai local avec un exemple Gitlab
Référentiel à importer : Example GitBook site using GitLab Pages
yum -y install git
git clone https://gitlab.com/pages/gitbook.git
cd gitbook
ls -la
docker run -it -p 4000:4000 -v $PWD:/gitbook node:latest bash
cd /gitbook
npm install gitbook-cli -g
gitbook install
gitbook serve
3.2. Pipeline GitLab CI
Fichier .gitlab-ci.yml
# requiring the environment of NodeJS 10
image: node:10
# add 'node_modules' to cache for speeding up builds
cache:
paths:
- node_modules/ # Node modules and dependencies
before_script:
- npm install gitbook-cli -g # install gitbook
- gitbook fetch 3.2.3 # fetch final stable version
- gitbook install # add any requested plugins in book.json
test:
stage: test
script:
- gitbook build . public # build to public path
only:
- branches # this job will affect every branch except 'master'
except:
- master
# the 'pages' job will deploy and build your site to the 'public' path
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- gitbook build . public # build to public path
artifacts:
paths:
- public
expire_in: 1 week
only:
- master # this job will affect only the 'master' branch
4. CI/CD Gitbook
4.1. Pipeline GitLab CI
Référentiel à importer : Gitbook Publication
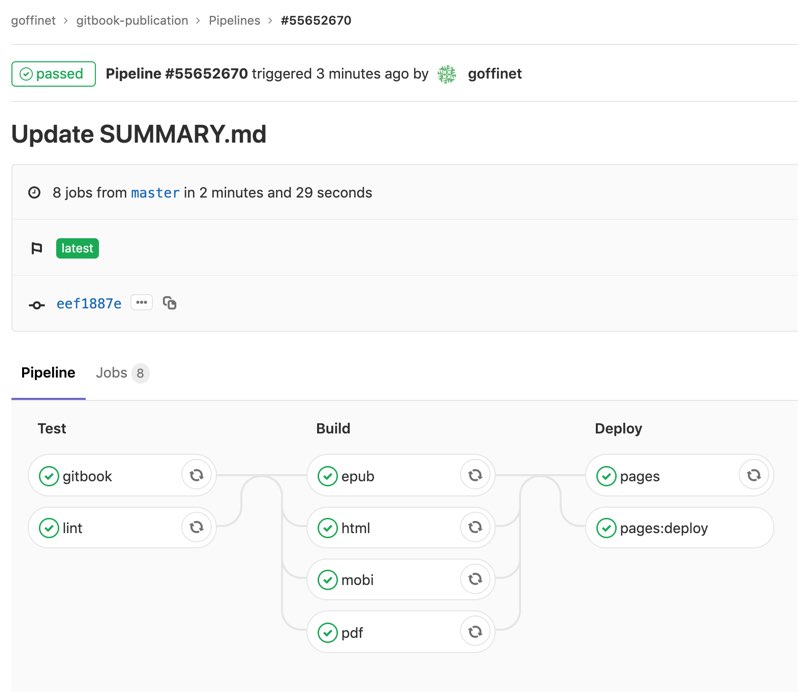
Fichier gitlab-ci.yml :
# This pipeline run three stages Test, Build and Deploy
stages:
- test
- build
- deploy
image: goffinet/gitbook:latest
# the 'gitbook' job will test the gitbook tools
gitbook:
stage: test
image: registry.gitlab.com/goffinet/gitbook-gitlab:latest
script:
- 'echo "node version: $(node -v)"'
- gitbook -V
- calibre --version
allow_failure: false
# the 'lint' job will test the markdown syntax
lint:
stage: test
script:
- 'echo "node version: $(node -v)"'
- echo "markdownlint version:" $(markdownlint -V)
- markdownlint --config ./markdownlint.json README.md
- markdownlint --config ./markdownlint.json *.md
allow_failure: true
# the 'html' job will build your document in html format
html:
stage: build
dependencies:
- gitbook
- lint
script:
- gitbook install # add any requested plugins in book.json
- gitbook build . book # html build
artifacts:
paths:
- book
expire_in: 1 day
only:
- master # this job will affect only the 'master' branch
allow_failure: false
# the 'pdf' job will build your document in pdf format
pdf:
stage: build
dependencies:
- gitbook
- lint
before_script:
- mkdir ebooks
script:
- gitbook install # add any requested plugins in book.json
- gitbook pdf . ebooks/${CI_PROJECT_NAME}.pdf # pdf build
artifacts:
paths:
- ebooks/${CI_PROJECT_NAME}.pdf
expire_in: 1 day
only:
- master # this job will affect only the 'master' branch
# the 'epub' job will build your document in epub format
epub:
stage: build
dependencies:
- gitbook
- lint
before_script:
- mkdir ebooks
script:
- gitbook install # add any requested plugins in book.json
- gitbook epub . ebooks/${CI_PROJECT_NAME}.epub # epub build
artifacts:
paths:
- ebooks/${CI_PROJECT_NAME}.epub
expire_in: 1 day
only:
- master # this job will affect only the 'master' branch
# the 'mobi' job will build your document in mobi format
mobi:
stage: build
dependencies:
- gitbook
- lint
before_script:
- mkdir ebooks
script:
- gitbook install # add any requested plugins in book.json
- gitbook mobi . ebooks/${CI_PROJECT_NAME}.mobi # mobi build
artifacts:
paths:
- ebooks/${CI_PROJECT_NAME}.mobi
expire_in: 1 day
only:
- master # this job will affect only the 'master' branch
# the 'pages' job will deploy your site to your gitlab pages service
pages:
stage: deploy
dependencies:
- html
- pdf
- mobi
- epub # We want to specify dependencies in an explicit way, to avoid confusion if there are different build jobs
script:
- mkdir .public
- cp -r book/* .public
- cp -r ebooks/* .public
- mv .public public
artifacts:
paths:
- public
only:
- master
4.2. Déploiement sur Netlify
...
5. CI/CD Jekyll
5.1. Pipeline GitLab CI
Référentiel à importer : Jekyll good-clean-read
Fichier gitlab-ci.yml :
image: ruby:2.3
variables:
JEKYLL_ENV: production
LC_ALL: C.UTF-8
before_script:
- bundle install
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- bundle exec jekyll build -d public
artifacts:
paths:
- public
only:
- gitlab
6. CI/CD Mkdocs
6.1. Pipeline GitLab CI
Référentiel à importer : mkdocs-material-boilerplate
Fichier gitlab-ci.yml :
image: python:3.6-alpine
before_script:
- pip install --upgrade pip && pip install -r requirements.txt
pages:
script:
- mkdocs build
- mv site public
artifacts:
paths:
- public
only:
- master
6.2. Déploiement sur Netlify

7. CI/CD Maven - Apache Tomcat
7.1. Premier exemple
Exemple CI/CD avec Maven, lecture de l'exemple et application selon le document Maven in five minutes.
Créer un dépôt sur Gilab et le cloner localement.
Importer une clé SSH.
Image Docker maven.
Pipeline :
- test
- build
Essai local
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.mycompany.app -DartifactId=my-app -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DarchetypeVersion=1.4 -DinteractiveMode=false
cd my-app
docker run -it -v $PWD/my-app:/my-app maven bash
exit
Pipeline GitLab CI
Fichier .gitlab-ci.yml
image: maven:latest
build:
stage: build
script:
- mvn package
artifacts:
paths:
- target
test:
stage: test
script:
- java -cp target/my-app-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.mycompany.app.App
Initialisation d'un repo gitlab
git init
git add *
echo "target" >> .gitignore
git add .gitignore
git remote add origin https://gitlab.com/account/project.git
git push -u origin master
7.2. Second exemple
Cette fois ci avec l'archétype Maven "Webapp" et une phase/job "deploy"
- test
- build
- deploy
Déploiement sur Tomcat
...
| Méthodes | Authentification |
|---|---|
| SSH et Bash | clé secrète |
| SCP | clé secrète |
| Text Manager avec curl | login/mot de passe |
Variables cachées
...
Gitlab Runner
Exécution sur un Gitlab-Runner qui héberge le serveur applicatif.
...
Avertissement Slack
...
Pipeline GitLab CI
...
8. Projets PHP
Test PHP projects using the Docker executor
# Select image from https://hub.docker.com/_/php/
image: php:latest
# Select what we should cache between builds
cache:
paths:
- vendor/
before_script:
- apt-get update -yqq
- apt-get install -yqq git libmcrypt-dev libpq-dev libcurl4-gnutls-dev libicu-dev libvpx-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libxpm-dev zlib1g-dev libfreetype6-dev libxml2-dev libexpat1-dev libbz2-dev libgmp3-dev libldap2-dev unixodbc-dev libsqlite3-dev libaspell-dev libsnmp-dev libpcre3-dev libtidy-dev
# Install PHP extensions
- docker-php-ext-install mbstring mcrypt pdo_pgsql curl json intl gd xml zip bz2 opcache
# Install & enable Xdebug for code coverage reports
- pecl install xdebug
- docker-php-ext-enable xdebug
# Install and run Composer
- curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php
- php composer.phar install
# Bring in any services we need http://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/docker/using_docker_images.html#what-is-a-service
# See http://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/services/README.html for examples.
services:
- mysql:5.7
# Set any variables we need
variables:
# Configure mysql environment variables (https://hub.docker.com/r/_/mysql/)
MYSQL_DATABASE: mysql_database
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: mysql_strong_password
# Run our tests
# If Xdebug was installed you can generate a coverage report and see code coverage metrics.
test:
script:
- vendor/bin/phpunit --configuration phpunit.xml --coverage-text --colors=never
9. Installation d'un serveur GitLab CE
On trouve plusieurs modes d'installation d'un serveur Gitlab :
- Installation par "Omnibus"
- Installation par les sources
- Déploiement avec Docker
Nous évoquons ici uniquement une installation par "Omnibus".
9.1. Omnibus
Omnibus GitLab est un Fork personnalisée du projet Omnibus de Chef qui utilise des composants de Chef comme les cookbooks et les recipes pour exécuter la tâche de configuration d'un serveur GitLab sur un ordinateur. Le dépôt Omnibus GitLab sur GitLab.com héberge tous les composants nécessaires à Omnibus. Cela comprend les parties d'Omnibus qui sont nécessaires pour construire le paquet, comme les configurations et les métadonnées du projet, et les composants liés à Chef qui seront utilisés sur l'ordinateur après l'installation.
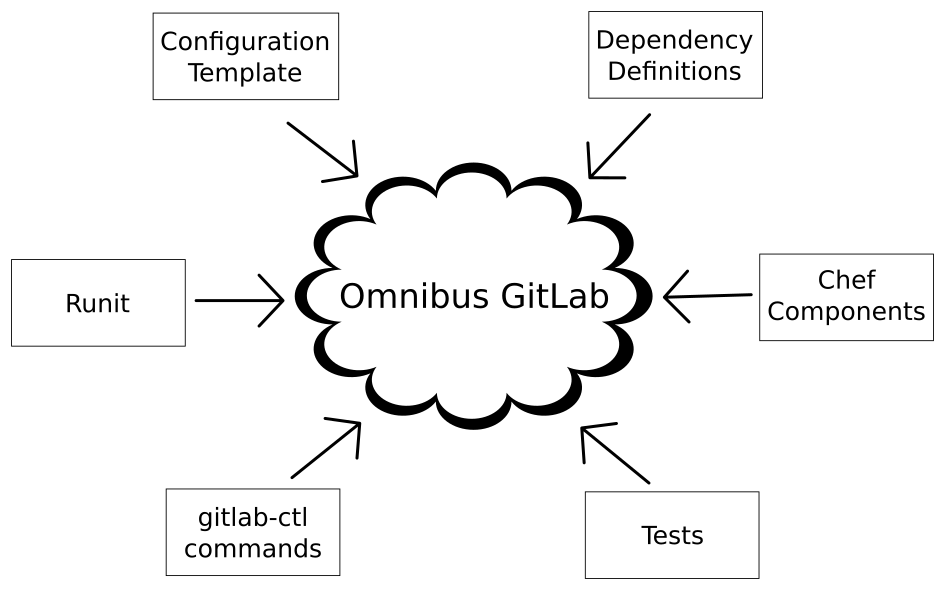
Source de l'image : Omnibus GitLab Architecture and Components
9.2. Installation par Omnibus
Nous choisissons une installation par Omnibus.
Le variable ${EXTERNAL_URL} décide l'usage de HTTP ou HTTPS.
On installe un packet rpm sur Centos 7.
#tls=no
mkdir tmp ; cd tmp
export PUBLIC_IPV4=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)
export DNSDOMAIN="gitlab.${PUBLIC_IPV4}.nip.io"
if [[ "$tls" == "no" ]] ; then
export EXTERNAL_URL="http://${DNSDOMAIN}"
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 1000 -nodes -subj '/CN=$DNSDOMAIN'
else
export EXTERNAL_URL="https://${DNSDOMAIN}"
fi
export GITLAB_VERSION="13.7.1"
yum -y install policycoreutils-python
yum -y install wget
wget --content-disposition https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/packages/el/7/gitlab-ce-${GITLAB_VERSION}-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm/download.rpm
export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"
echo 'export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"' >> .bashrc
rpm -Uvh gitlab-ce-${GITLAB_VERSION}-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm
A la première connexion sur l'interface Web, vous décidez d'un mot de passe root. Par défaut, les utilisateurs peuvent s'auto-enregistrer. Un compte comme root admet ces nouvelles demandes et octroie les droits aux utilisateurs. Ce comportement peut facilement être diminué ou être augmenté en terme de sécurité.
Notes:
It seems you haven't specified an initial root password while configuring the GitLab instance.
On your first visit to your GitLab instance, you will be presented with a screen to set a
password for the default admin account with username `root`.
gitlab Reconfigured!
*. *.
*** ***
***** *****
.****** *******
******** ********
,,,,,,,,,***********,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,*********,,,,,,,,,,,
.,,,,,,,,,,,*******,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,*****,,,,,,,,,.
,,,,,,,****,,,,,,
.,,,***,,,,
,*,.
_______ __ __ __
/ ____(_) /_/ / ____ _/ /_
/ / __/ / __/ / / __ `/ __ \
/ /_/ / / /_/ /___/ /_/ / /_/ /
\____/_/\__/_____/\__,_/_.___/
Thank you for installing GitLab!
En cas de problème : How to reset your root password
9.3. Mise-à-jour
La mise à jour consiste à installer un nouveau packet dans la nouvelle version.
export GITLAB_VERSION="13.7.2"
yum -y install policycoreutils-python
yum -y install wget
wget --content-disposition https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/packages/el/7/gitlab-ce-${GITLAB_VERSION}-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm/download.rpm
export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"
echo 'export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"' >> .bashrc
rpm -Uvh gitlab-ce-${GITLAB_VERSION}-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm
9.4. Post-installation
- Mail : installation postfix 'Internet Site' ou configure an external SMTP server
- LDAP
- Stocker les données dans des autres emplacements ou encore sur Stackoverflow
- Démarrer les services après les points de montage
- Les emplacements des données
- Configurer la timezone
- Modifier le logo
9.5. Modèle AWS CloudFormation
...
10. Administration d'un serveur GitLab
10.1. Emplacement des fichiers
- L'emplacement par défaut des données :
/var/opt/gitlab/git-data - Fichier de configuration du serveur :
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
10.2. Gestion du serveur
- Reconfiguration du serveur :
gitlab-ctl reconfigure - Statut du serveur :
gitlab-ctl status - Tail sur les logs :
gitlab-ctl tail - Démarrer, arrêter ou redémarrer le serveur ou des services :
gitlab-ctl start|stop|restart
10.3. Backups
11. Installation et configuration de Gitlab Runner
11.1. Installation
Téléchargement des dépôts de paquetage Gitlab: Install GitLab Runner
Pour Debian/Ubuntu :
curl -L https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/runner/gitlab-runner/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
Pour RHEL/CentOS/Fedora
curl -L https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/runner/gitlab-runner/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
Installation de Gitlab Runner.
sudo apt-get install gitlab-runner || sudo yum install gitlab-runner
11.2. Enregistrement auprès du serveur Gitlab
Pour que votre instance devienne un noeud d'exécution Gitlab, veuillez vous rendre sur la page Settings/CI CD/Runners du projet Gitlab. Vous y trouverez le token qui permettra à votre instance de se faire connaître auprès du projet Gitlab.
sudo gitlab-runner register \
--non-interactive \
--url "https://gitlab.com/" \
--registration-token "$PROJECT_REGISTRATION_TOKEN" \
--executor "docker" \
--docker-image alpine:3 \
--description "docker-runner" \
--tag-list "docker,aws" \
--run-untagged \
--locked="false"
Un fichier de configuration sera créé à l'endroit /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml.
Ensuite, démarrer le logiciel.
sudo gitlab-runner start
En revenant sur la page Settings/CI CD/Runners du projet Gitlab, on devrait y trouver la liste des "runners" avec l'instance.
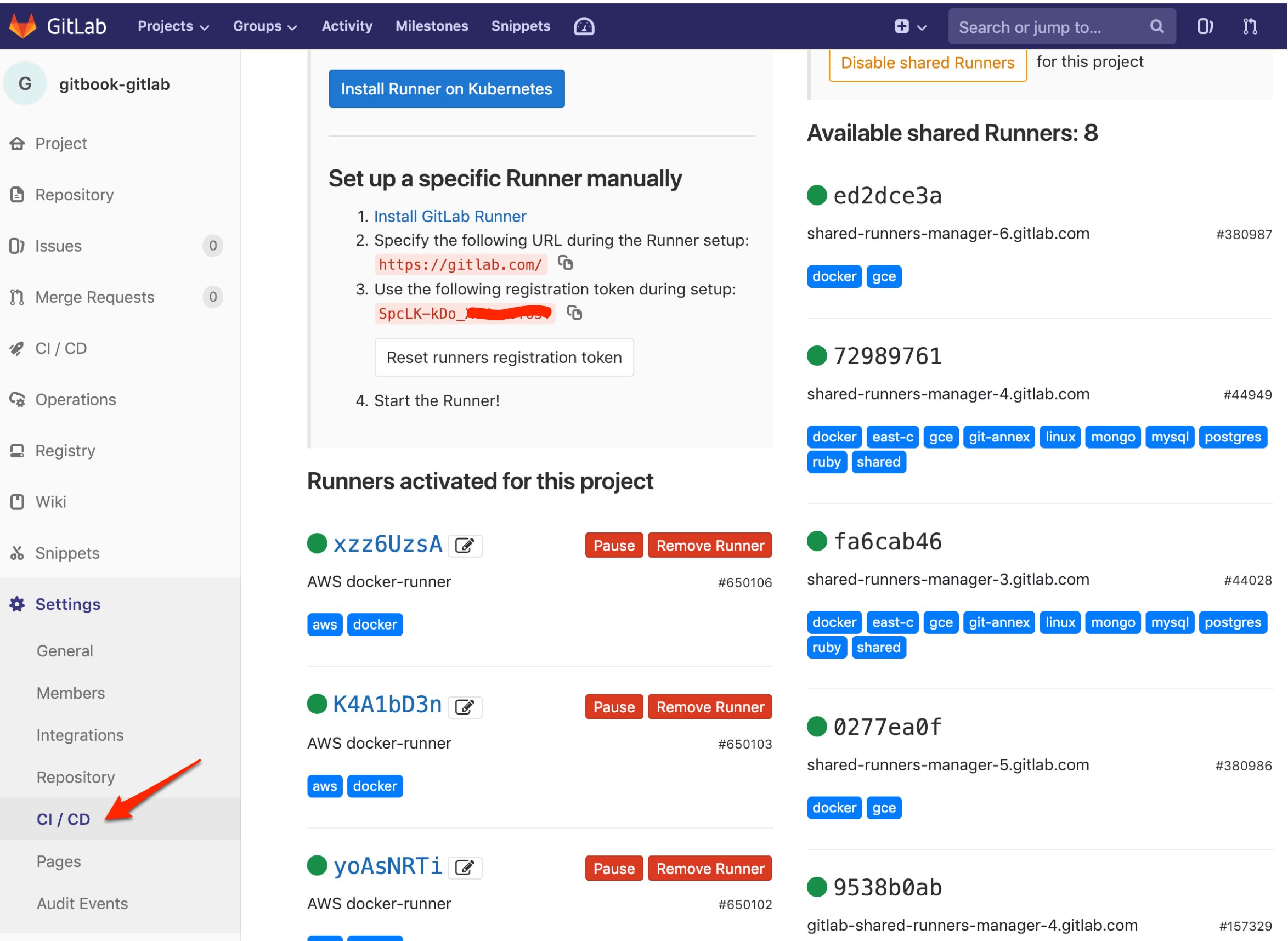
12. Scénario de vie / Orchestration
12.1. Approvisionnement automatique du runner
Installation, enrigistrement et démarrage de gitlab runner
Veuillez vérifier tous les paramètres.
#!/bin/bash
# Gitlab runner installation
PROJECT_REGISTRATION_TOKEN=$1
apt-get update && apt-get -y upgrade
apt-get -y install curl
curl -L https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/runner/gitlab-runner/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
apt-get -y install gitlab-runner
gitlab-runner register \
--non-interactive \
--url "https://gitlab.com/" \
--registration-token "$PROJECT_REGISTRATION_TOKEN" \
--executor "docker" \
--docker-image alpine:3 \
--description "AWS docker-runner" \
--tag-list "docker,aws" \
--run-untagged \
--locked="false"
gitlab-runner start
Installation de Docker CE
# Docker installation
apt-get -y install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg2 \
software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"
apt-get update
apt-get -y install docker-ce
12.2. Approvisionnement d'instance via cloud-init
...
12.3. Approvisionnement d'instances via Kubernetes
...